StringBuffer class
You can create a mutable string using the StringBuffer class. This is the only difference between the string class and the StringBuffer class that can be changed.
Constructors
Below are the constructors that can be used in the StringBuffer class-
- StringBuffer()- it will create an empty string buffer with the initial capacity of 16.
- StringBuffer(String str)- it will create a string buffer with the specified string.
- StringBuffer(int capacity)- it will create an empty string buffer with the specified capacity as length.
Methods
You can use the below methods to change and modify the string.
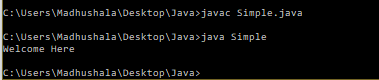
append() method- this method will append the provided string with this string. You can use this method for method overloading.
Example-
class Simple{
public static void main(String args[]){
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer("Welcome");
sb.append(" Here");
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
Output-
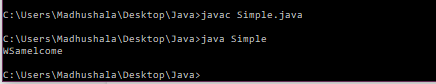
insert() method- this method will insert the provided string to another string at the given position.
Example-
class Simple{
public static void main(String args[]){
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer("Welcome ");
sb.insert(1,"Sam");
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
Output-
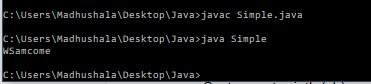
replace() method- this method will allow you to replace the specified string from the provided beginIndex and endIndex.
Example-
class Simple{
public static void main(String args[]){
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer("Welcome ");
sb.replace(1,3,"Sam");
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
Output-
delete() method- this method will allow you to delete the specified string from the provided beginIndex and endIndex.
Example-
class Simple{
public static void main(String args[]){
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer("Welcome ");
sb.delete(1,3);
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
Output-
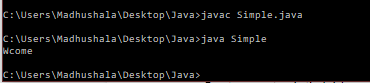
reverse() method- this method will reverse the current string.
Example-
class Simple{
public static void main(String args[]){
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer("Welcome ");
sb.reverse();
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
Output-
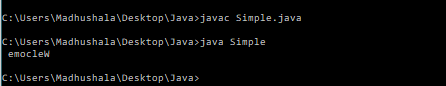
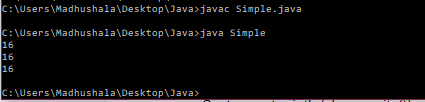
capacity() method- this method will return the buffer’s current capacity.
Example-
class Simple{
public static void main(String args[]){
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer();
System.out.println(sb.capacity());
sb.append("welcome");
System.out.println(sb.capacity());
sb.append("hello");
System.out.println(sb.capacity());
}
}
Output-